The Environment
Energy
KPI
Responsible Departments
Our position and Targets
Review of FY 2022 Activities
Introduction of Initiatives
Future challenges
KPI
Move the screen to the left or right to see the table information
| Item | FY 2021 results | FY 2022 results |
|---|---|---|
| Total energy consumption |
(Consolidated) 1,879,142MWh * Crude oil equivalent: 474,991 KL |
(Consolidated) 1,837,184MWh * Crude oil equivalent: 464,331 KL |
| Total renewable energy consumption | (Consolidated)28,669MWh | (Consolidated)41,352MWh |
| Total external energy consumption * Reported as Scope 3 (Other emissions) |
56,735,901 MWh | 60,455,880 MWh |
Responsible Departments
Each business location
- Activities are conducted by each business location, and the Global Warming Countermeasures Committee that the Environmental Protection Promotion Department serves as a secretariat for implements company-wide policy discussions and activities.
In 2022, the committee structure was revised and changed to the Carbon Neutrality Promotion Committee.
Our position and Targets
Why is “Energy” a critical issue to be addressed?
Explanation of the reason and background
The Yokohama Rubber Group, which conducts production activities in twelve different countries (Japan, United States, the Philippines, China, Thailand, Russia, Vietnam, India, Taiwan, Indonesia, Mexico and Israel) around the world, uses a large volume of energy in the production process. We define energy as one of the most critical issues for us to address since the reduction of energy consumption will accelerate the solution of climate change issues posing a global-scale problem and the effective use of depleting resources while at the same time reducing costs.
Our policy and position relating to energy
The Yokohama Rubber Group states its environmental position in the "Yokohama Rubber Company-wide Environmental Policy", we work to minimize our environmental impacts. To that end, in addition to developing and adopting environment-friendly technologies from the design and manufacturing stage, we work to use energy in the most sustainable and appropriate manner possible and to reduce energy consumption throughout the value chain while collaborating with people involved in the provision of related products and services.
We will keep trying to use energy most wisely while making efforts to reduce energy use in accordance with international protocols concerning the proper use of energy, the regulations of countries where we operate (laws equivalent to the Act on the Rational Use of Energy, and the Act on Promotion of Global Warming Countermeasures of Japan), and the policies of related organizations.
We will keep trying to use energy most wisely while making efforts to reduce energy use in accordance with international protocols concerning the proper use of energy, the regulations of countries where we operate (laws equivalent to the Act on the Rational Use of Energy, and the Act on Promotion of Global Warming Countermeasures of Japan), and the policies of related organizations.
Vision and targets
In line with the globally shared goal of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050, the Yokohama Rubber Group is working to reduce total greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions as an indicator for reducing energy consumption.
- Long-term target:
- Achieve net zero CO2 emissions (carbon neutrality) in our activities by 2050
- Mid-term target:
- Reduce CO2 emissions from company activities by 38% by 2030 compared to fiscal 2013
※This activity is the same level of effort as our goal of 28% reduction by 2030 (compared to 2019). - Encourage suppliers to collaborate with us in line with our targets.
- Reduce CO2 emissions from company activities by 38% by 2030 compared to fiscal 2013
Measures to pursue our vision
We will implement the following measures aimed at promoting the appropriate use and reduction of energy through our overall business activities:
- Promote a modal shift in logistics.
- Conduct energy management in production
Promote the effective use of energy through system improvements, cost saving improvements, process improvements, the development of management systems, the introduction of production systems, and the introduction of new energy (including renewable energy) in the production process. - Promote energy reduction activities by establishing seven energy-saving subcommittees.
- Promote the development and sales of eco-friendly products in order to reduce the amount of energy use resulting from product use.
Review of FY 2022 Activities
In Japan, Yokohama Rubber achieved an 18% reduction in GHG emissions on a non-consolidated basis compared with 2013 levels, as a result of promoting system improvements (development of energy-saving vulcanization system, and utilization of co-generation), cost saving improvements (increased use of LEDs, and improvement of facility operation rate), process improvements (optimization of rubber kneading process), and the introduction of new energy (introduction of solar power generation system).
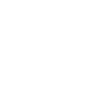
Overall picture of the environmental burden in Japan
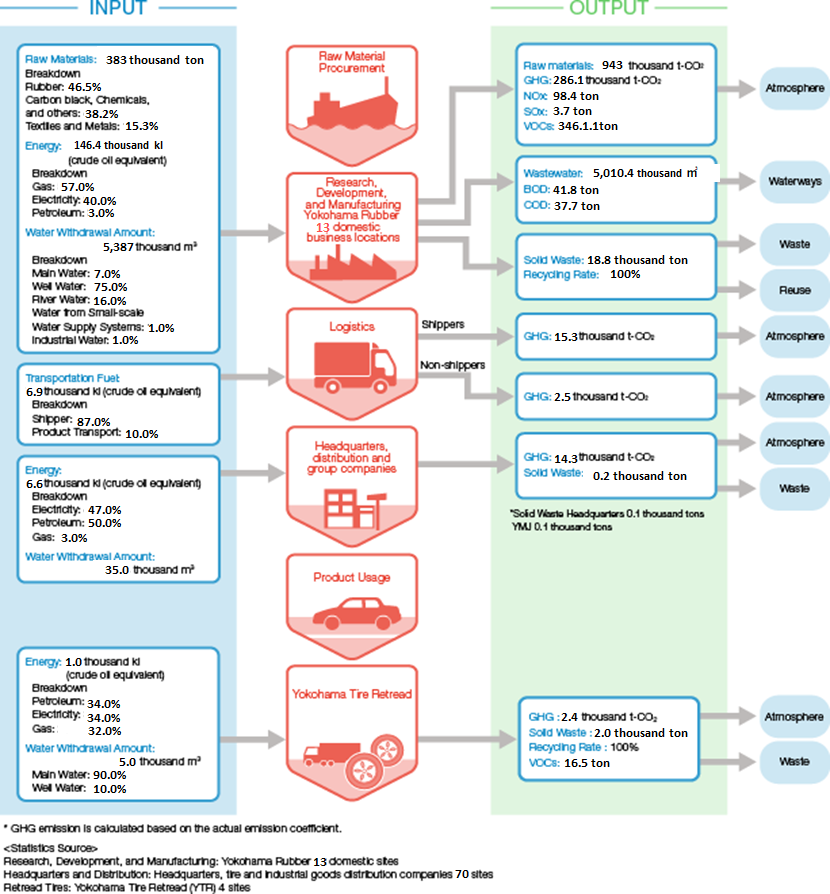
Overall picture of the environmental burden overseas
Introduction of Initiatives
Reduction of energy usage and CO2emissions in logistics
- Target: We are working on the reduction of CO2 emissions in line with the corporate mission of the Yokohama Rubber Group.
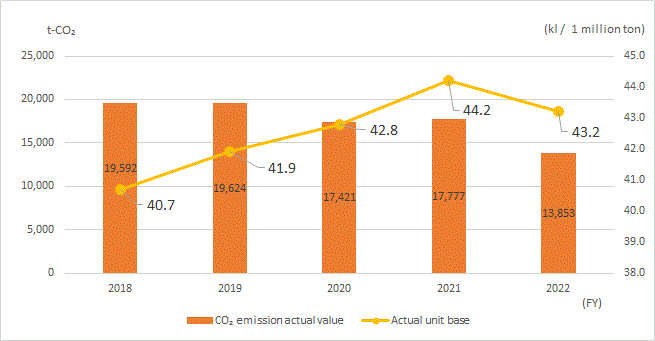
- Results: In FY2022, we continued to review transportation routes, reduce warehouse transportation volume, and improve loading efficiency, achieving 22% reduction from the previous year with emissions being 13,853t-CO2.
The standard energy consumption unit improved by 2.3% to 43.2 kl/million ton-kilometer.
CO2 emissions and emissions per unit of output
* Yokohama Rubber on a non-consolidated basis

Rail transport for Shinshiro to Kyushu shipments
Energy management
- Visualization of energy use
- Control of peak power by means of demand control equipment
- Heat insulation for plant building roofs
- Reduction of boiler fuel by updating the water supply system of boiler facilities to reduce the boiler drainage rate (introduction of a device to automatically control the number of air compressors in operation)

Boiler facilities Water supply system
Switched the agitation motor from an air type to an electric type.

Air motor

Electric motor
Conducted diagnosis on the steam drain trap to control steam energy loss.

Steam drain trap (Upper photo: defective trap, lower photo: new trap)
Controlled air leakage loss by managing (closing) the air source valve when not in operation.

Air valve management during non-operating hours (closed)
Installed the detachable heat insulation material at the uninsulated part of the once-through boiler to control heat radiation loss.


Removable heat insulator
Used air leak visualization equipment to detect air and steam leaks in order to control loss increase resulting from air leaks at each plant in Japan.
Energy loss was improved by branching the piping system of steam-type unit heaters and adding individual valves based on the result of manufacturer energy conservation diagnosis.

Separated the steam system and installed a motor valve
Liquefaction efficiency of air conditioning refrigerant was improved by installing a high-efficient refrigerant liquefaction heat exchanger on the outdoor compressor unit of the air conditioner.

High-efficiency refrigerant liquefaction heat exchangers
High-efficiency refrigerant liquefaction heat exchangers were additionally installed on air conditioners and coolers to improve their heat-exchange efficiency.
Full Operation of Co-generation Systems
At tire plants using a large volume of energy and steam, it is possible to achieve a significant reduction in CO2 emissions through the adoption of co-generation systems that supply energy and steam simultaneously. As of 2022, the co-generation system is operating at three domestic plants. As a result of continuous 24-hour operations, 72% of the energy and nearly all of the steam used by these plants are now supplied by the co-generation systems, contributing to the reduction in CO2 emissions and the reduction of the amount of power purchased from the electric company and power consumption during peak time. This system has also been adopted at our Thai plant.

Mie Plant co-generation system

Mishima Plant co-generation system

Shinshiro Plant co-generation system

Thai Plant co-generation system
Improving the efficiency of motors and pumps for production equipment
The booster pumps of the pressure testing machine were switched to air hydro pumps with intermittent operation control, and the duct fan V-belt was replaced with an energy-saving type, which has led to an effective reduction of power consumption.

Air hydro pumps
The hydraulic unit for a multi-axis automatic lathe has been converted to an inverter type to reduce power consumption during standby time.

Hydraulic unit inverter conversion
We are switching other existing motors to high-efficiency ones.

High-efficiency motor

High-efficiency motor
Improving the efficiency of cooling-water pumps for production equipment
In conjunction with the renewal of the calendar equipment hotbed device, the heat exchange system was changed (from direct mixing to indirect heating) to reduce steam consumption.
In winter, when the water temperature in the cooling-water tank drops, the circulating cooling tower equipment is deactivated to reduce electricity consumption.
In winter, when the water temperature in the cooling-water tank drops, the circulating cooling tower equipment is deactivated to reduce electricity consumption.

Cooling-water pump

Optimizing the chiller tank
Adoption of LED lights
We are replacing ceiling lights, in our domestic and overseas sites, which were previously mercury or fluorescent lights, with LED lights or other high-efficiency lighting products. In addition, the use of human detecting sensor control has been promoted, achieving the highly effective reduction of electricity consumption.

Conversion to motion sensors and LEDs

Conversion to motion sensors and LEDs

Mercury lighting → LED lighting

Replacement of lighting
Solar power generation
We are proceeding with the installation of environment-friendly solar power (renewable energy) generation facilities.
Solar power generation was introduced in the plants in India and China (Suzhou) in FY2017, in the plant the Philippines in FY2019, and in the Shinshiro-Minami Plant in FY2023.
Solar power generation was introduced in the plants in India and China (Suzhou) in FY2017, in the plant the Philippines in FY2019, and in the Shinshiro-Minami Plant in FY2023.

Solar power generation (Suzhou, China) installed capacity: 3,000 kw

Solar power generation (Hangzhou, China) installed capacity: 80 kw

Solar power generation (India) installed capacity: 200 kw

Solar power generation (Mie) installed capacity: 500 kw

Solar power generation (Philippines) installed capacity: 4,000 kw

Solar power generation (Shinshiro-Minami)installed capacity:1,040kw
Biogas
Food waste used to go to a landfill at the Tirunelveli Plant in India. In addition to a hygiene-related issue, the generation of methane, whose emission factor is 25 times higher than that of CO2, used to be a persistent problem. To cope with this, we built a biogas plant and began to process 250kg of food waste per day to generate gas in FY2019. In 2022, LPG gas consumption was reduced by 352kg, resulting in a reduction of 1.06t-CO2.

Energy-saving monthly activities
Under the slogan of "Let us care for our region and earth: Start winter energy saving toward carbon neutrality," after sharing recognition on the significance of energy saving, that is, "strengthening corporate competitiveness through cost reductions, responding to fossil fuel depletion, reducing impact on the global environment, and fulfilling corporate social responsibility," and after carrying our adequate preparations, the production department, the equipment maintenance department, and administration department made concerted and united efforts and accumulated multiple small effects and results during the "Energy-Saving Month" of February. For example, in an energy-saving diagnosis, the maintenance department conducted inspection on equipment and found steam and air leakage, and repaired the leaks.

Education activities during the Energy Saving Month
Leakage inspection and visualization

Leak repair
Energy saving subcommittee
An "energy saving subcommittee" meeting was organized by energy saving staff from domestic plants to follow up on annual energy saving reduction plans, and the status of investment in energy-saving equipment and progress. The committee also share useful information by introducing improvement cases at each plant to further promote energy reduction.

Activities of the Energy Saving Subcommittee
Activities to enhance energy management based on guidance from consultants
We are working on the enhancement of energy management (adoption of a just-in-time system for energy) through various means such as reductions of energy loss in line with production variation (switching equipment on and off).
The bases in Japan and overseas benefit from guidance provided by consultants every year.
The bases in Japan and overseas benefit from guidance provided by consultants every year.
Future challenges
We are going to continue to expand the introduction of co-generation systems to achieve the reduction of total energy usage.
Regarding the increase of renewable energy usage ratio, we are going to expand the introduction of solar power generation, etc. and increase the ratio of renewable energy used at our bases.
Regarding the increase of renewable energy usage ratio, we are going to expand the introduction of solar power generation, etc. and increase the ratio of renewable energy used at our bases.