Troubleshooting
Leaking from hose
Burst at the hose body
(1) Symptom: The reinforcement wire is completely broken diagonally or is exploded out.

Cause:
The operating pressure has exceeded the minimum burst pressure of the hose.
Remedy:
Check the operating pressure (relief set pressure / impact pressure) and reselect the appropriate hose.
(2) Symptom: The reinforcement wire is randomly fractured.

Cause:
Wire fractured due to continuous pressure applied beyond the allowable pressure.
Remedy:
Check the pressure and frequency and re-select the appropriate hose.
(3) Symptom: The outer cover has been damaged and the reinforcement wire is severely corroded and broken.

Cause:
The hose has been exposed to salt water and/or industrial water.
The hose is not compatible with the application (steam, chemical, acid) being used, and the application is causing the reinforcement wire to rust.
Remedy:
Use hose protection material or apply sealant to the hose in order to prevent the outer cover from being damaged.
By taking such countermeasures, you can prevent corrosive materials from penetrating into the hose and attacking the reinforcement wire.Check the application and select the appropriate hose suitable for steam, chemical or acid.
*Our hose protection material lineup is listed on page 7 of our catalog.
Flattened out hose
(1) Symptom: The hose is flattened out due to external pressure.

Cause:
Poor routing of the hose.
If the hose is flattened out, it will damage the outer cover and also cause the reinforcement wire to break.
Remedy:
Identify what is causing pressure on the hose and remove such cause.
Also protect the outer cover by using hose protection material.
*Our hose protection material lineup is listed on page 7 of our catalog.
(2) Symptom: The hose is kinked.

Cause:
Poor routing of the hose.
Remedy:
Use swivel fittings or joints to prevent the hose from being kinked.
Thermoplastic hoses are more likely to be kinked
(3) Symptom: The hose is twisted and deformed.

Cause:
Poor routing of the hose.
Remedy:
Take extra care not to twist the hose when installing the hose assembly.
Reinforcement wire may be damaged when the hose is twisted.
Blistering of the hose
(1) Symptom: The inner tube has bulge.

Cause:
Residual air in the piping has effused through the hose tube and formed an air pocket in between the reinforcement wires.
Remedy:
Remove the residual air before using the hose.
(2) Symptom: The inner tube is partially gouged.
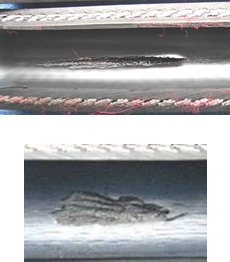
Cause:
A concentrated high-velocity fluid stream is attacking the inner tube.
Remedy:
Re-route the hose so that the hose assembly is not bent too tight.
Also, determine the most appropriate hose size based on the velocity and volume of the fluid.
*The recommendation chart is shown in page 5 of our catalog to assist you in choosing the right hose.
Hose crack
(1) Symptom: The outer cover and inner tube is excessively hard and cracked.
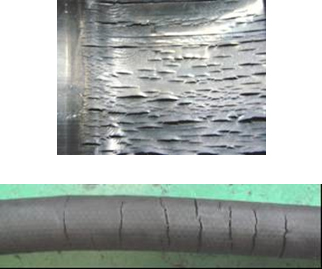
Cause:
There was an excessive rise in the fluid temperature or in the atmosphere temperature
Deterioration by ozone attack.
Application incompatibility.
Remedy:
Select the appropriate hose based on the working temperature or lower the temperature by using an oil cooler.
Use a protector to prevent exposure to sunlight.
Use the hose that is compatible with the application.
(2) Symptom: The outer cover is excessively hard and cracked.

Cause:
The hose has been exposed to salt water, industrial water, and/or sunlight.
Remedy:
Use hose protection material or apply sealant to the hose in order to protect the outer cover.
*Our hose protection material lineup is listed on page 7 of our catalog
Outer cover abrasion
(1) Symptom: The outer cover is worn out.
Cause:
The hose has come into contact with other objects such as other hoses, metal edges, and etc.
Remedy:
Replace the hose.
Use alternative hose with superior abrasion resistant cover.
Use hose protection material.
Leaking from fitting
Leakage from the fitting end
(1) Symptom: The outer cover and inner tube is excessively hard and cracked.
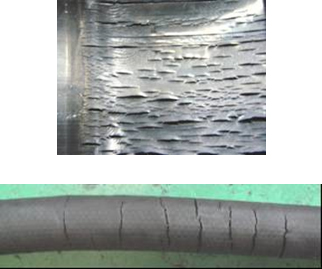
Cause:
There was an excessive rise in the fluid temperature or in the atmosphere temperature.
Remedy:
Select the appropriate hose based on the working temperature or lower the temperature by using an oil cooler.
(2) Symptom: The hose is bent to an extreme near the hose end.

Cause:
Poor routing of the hose.
Remedy:
Use swivel fittings or joints to prevent the hose from being bent.
(3) Symptom: The hose is twisted and deformed near the hose end.

Cause:
Poor routing of hose.
If the hose is twisted near the hose end, it will cause the hose to break and leak.
Remedy:
Take extra care not to twist the hose when installing the hose assembly.
You can also use two wrenches when installing the hose assembly to prevent it from being twisted.
Leakage from sealing surface of the fitting
(1) Symptom: Over or under tightening of torque.
Cause:
Over or under tightening of torque is applied to the fitting.
Remedy:
Tighten the fitting according to the appropriate torque.
*The recommendation chart is shown in page 4 of our catalog to assist you in choosing the appropriate torque.
(2) Symptom: Foreign substance trapped into the fitting.

Cause:
The sealing surface of the fitting is contaminated and/or damaged.
Remedy:
Remove the foreign substance and check to see the sealing surface is not damaged.
Take extra care not to contaminate the sealing surface.
(3) Symptom: O-ring size is not appropriate.
Cause:
The specification and / or size of the O-ring is incorrect.
Remedy:
Use the correct O-ring for the fitting.
For more details of our O-rings, check page 82 of our catalog.