The Environment
Water and wastewater
KPI
Responsible Departments
Stance and Target
Review of FY 2021 Activities
Introduction of Initiatives
Issues and Future Improvement Measures
KPI
Move the screen to the left or right to see the table information
| Item | FY 2020 results | FY 2021 results |
|---|---|---|
| Water intake | (Consolidated) 8,036 thousand m3 | (Consolidated) 8,494 thousand m3 |
| Percentage of recycled and reused water (Circulating water/water intake ratio) |
(Consolidated) 141% | (Consolidated) 144% |
| Water sources significantly affected by water intake |
(Consolidated) NA <Endangered species> There are endangered species in the Miya River (Mie), Kanogawa River (Mishima), and Kaname River (Hiratsuka) (red list of threatened species) <Intake of water from protected areas> Not applicable. There is no intake of water from protected areas. |
(Consolidated) NA <Endangered species> There are endangered species in the Miya River (Mie), Kanogawa River (Mishima), and Kaname River (Hiratsuka) (red list of threatened species) <Intake of water from protected areas> Not applicable. There is no intake of water from protected areas. |
Responsible Departments
Each business location
- Performance is managed by the Production Environmental Task Force.
Stance and Target
Why is “Water” a critical issue to be addressed?
Explanation of the reason and background
Yokohama Rubber Group’s use of water consists of two forms: the use of water such as cooling water for boilers and production facilities at production bases (direct use) and the use of water at suppliers of raw materials etc. (indirect use).
For direct use, the risks (physical, regulatory, reputation risk, etc.) vary depending on the region of each business location. For this reason, we believe that it is important to effectively use precious water resources in line with the characteristics of each production base.
In addition, for the indirect use of water in the production process for raw materials such as natural rubber as well, we believe that it is necessary to confirm the situation and take the appropriate responses as necessary. This is based on our stance that if it is not possible to procure raw materials due to water-related risks at suppliers, this could directly result in serious problems that affect our operations.
For direct use, the risks (physical, regulatory, reputation risk, etc.) vary depending on the region of each business location. For this reason, we believe that it is important to effectively use precious water resources in line with the characteristics of each production base.
In addition, for the indirect use of water in the production process for raw materials such as natural rubber as well, we believe that it is necessary to confirm the situation and take the appropriate responses as necessary. This is based on our stance that if it is not possible to procure raw materials due to water-related risks at suppliers, this could directly result in serious problems that affect our operations.
Water use policy
Our domestic bases have rich water resources, and while we use these resources effectively as a recycled resource*, there are areas with water use constraints among our overseas business locations. For this reason, it is necessary to conduct water risk assessments in these areas and work to ensure that water is properly managed. We also believe that it is necessary to confirm the state of water use at suppliers and work together to adopt countermeasures in the event of water risks arising.
For this reason, we decided on a policy after reviewing the situation from fiscal 2015 to 2017. Furthermore, we will broadly release updates on the progress of these measures through means such as external questionnaires (CDP’s water, etc.) and our website.
For this reason, we decided on a policy after reviewing the situation from fiscal 2015 to 2017. Furthermore, we will broadly release updates on the progress of these measures through means such as external questionnaires (CDP’s water, etc.) and our website.
- We use water based on formal procedures such as agreements with regions (governments).
Water risk assessments
For many production base areas that use a lot of water, we use existing water risk assessment tools such as WRI’s Aqueduct to confirm potential water risks. Existing tools and local information are used to make judgments on comprehensive water risks.
Based on these results, we identify the highest risks among representative water risks for each business location (physical, regulatory, reputation risk, etc.), and consider measures that should be taken, starting with the highest priority risks.
Based on these results, we identify the highest risks among representative water risks for each business location (physical, regulatory, reputation risk, etc.), and consider measures that should be taken, starting with the highest priority risks.
Vision (attainment goal) / target
We will promote 3R initiatives for water at all of our business sites, including in the supply chain, and in each community to strive to use water soundly and conserve water resources. As a result, we will contribute to an appropriate water cycle on a global scale.
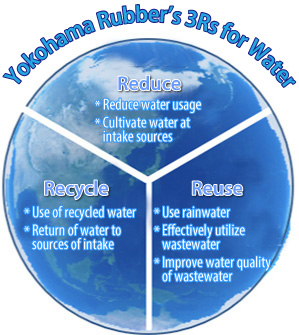
Measures for vision achievement
At domestic and overseas production bases, we conduct the following initiatives aimed at reducing water intake per unit of output by 1% year-on-year.
- Reinforce countermeasures for reducing water usage at sites with a high physical risk (water shortage)
- Thoroughly manage wastewater quality at sites with a high regulatory risk
- Enhancement of areas communication at sites with a high reputational risk
Review of FY 2021 Activities
A water risk assessment is conducted by incorporating local information with the results from WRI’s Aqueduct existing water risk assessment tool to manage risks by country in the categories of water volume risk (India, the Philippines, Italy), water quality risk (Japan, US, Thailand, Vietnam, Russia, Taiwan), and water volume and water quality risk (China, Indonesia). Reduction of 1% over the previous fiscal year was set.
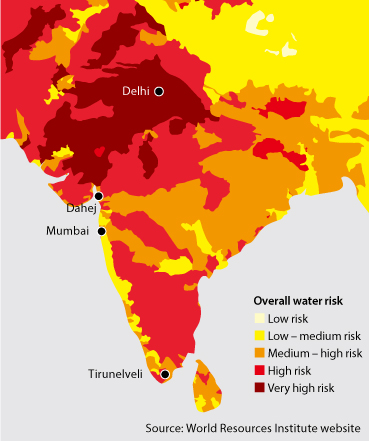
Level of water risk severity, based on World Resources Institute (WRI) data
- We completed a questionnaire relating to the CDP Water program and supply chain water usage once again in fiscal year 2021, and reported to suppliers. The breakdown of water withdrawal is 65% domestically and 35% internationally.
- We have implemented the effective use of water at all business locations through continuous leakage prevention and improvements to equipment using recycled water. In particular, water closed systems have been introduced at many overseas production bases in response to physical (water shortage) risks.
- We regularly check wastewater to ensure that there are no water quality problems.
We meet the water quality standards of the countries and regions where our bases are located.
Introduction of Initiatives
We have made capital investments at our Mie and Onomichi domestic production bases in leakage protection for facility pipes and recycled water use facilities.
As for our overseas production bases, we introduced a closed-loop system at the time of constructing our plant in India.
In Thailand and China, we collect rainwater and use it as cooling water and for restrooms.
In addition, water treatment facilities are being installed at all production bases to prevent deterioration in wastewater water quality.
As for our overseas production bases, we introduced a closed-loop system at the time of constructing our plant in India.
In Thailand and China, we collect rainwater and use it as cooling water and for restrooms.
In addition, water treatment facilities are being installed at all production bases to prevent deterioration in wastewater water quality.

Water treatment facilities at our production base in Italy
At our Nagano Plant, we recycle cooling water, etc., using a water recycling system.

Nagano-water recycling system
On the other hand, we are conducting "biodiversity conservation activities" in Mie, Shinshiro, Mishima, and Ibaraki to investigate the impact on the rivers where the water is discharged, and in Hiratsuka to investigate the impact on the rivers where the well water comes from.
Issues and Future
Improvement Measures
A framework will be established for the assessment of global data on water use, and the following initiatives will be implemented.
- Formulation of Yokohama Rubber Group standards (guidelines) for the proper management of water
- Enhancing internal awareness of the water initiatives and the need for these initiatives
- Joint implementation of water initiatives throughout the supply chain